H2 Biology (Syllabus 9744)
H2 Biology - Introduction
Candidates will be assumed to have knowledge and understanding of O-Level Biology, as a single subject or as part of a balanced science course.
The syllabus has been arranged in the form of Core and Extension content to be studied by all candidates. The syllabus emphasizes the applications of biology and the impact of recent developments on the needs of contemporary society.
Experimental work is an important component and should underpin the teaching and learning of biology.
The value of learning H2 Biology ultimately hinges on the development of a scientific mind and disposition while addressing the broader questions of what life is and how life is sustained. The Science Curriculum Framework developed by the Ministry of Education elaborates on the development of the scientific mind and disposition.
Through the study of the H2 Biology course, students will be prepared for life science-related courses at university and, consequently, careers that are related to this field.
Aims
The syllabus aims to:
- provide students with an experience that develops their interest in biology and builds the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary for further studies in related fields
- enable students to become scientifically literate citizens who are well-prepared for the challenges of the 21st century
- develop in students the understanding, skills, ethics and attitudes relevant to the Practices of Science, including the following:
- understanding the nature of scientific knowledge
- demonstrating science inquiry skills
- relating science and society
- address the broader questions of what life is and how life is sustained, including:
- understanding life at the cellular and molecular levels, and making connections to how these micro-systems interact at the physiological and organismal levels
- recognising the evolving nature of biological knowledge
- stimulating interest in and demonstrating care for the local and global environment.
Curriculum Framework
The rapid progress in the field of life sciences poses a challenge for Biology education, especially in terms of designing a framework that integrates fundamental knowledge, skills and attitudes. With this in mind, this syllabus has adopted a framework that will chart a new direction for Biology education. An overview of this framework is depicted in Fig. 1: H2 Biology Curriculum Framework
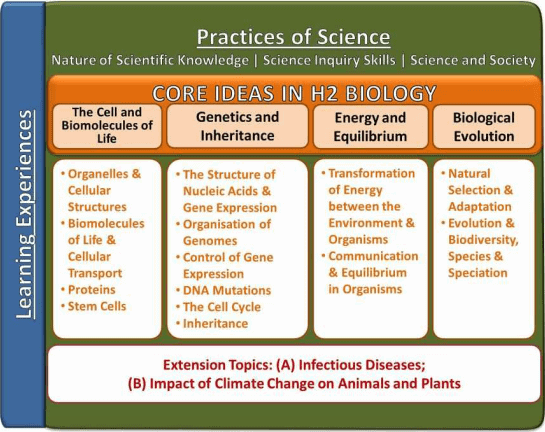
The Practices of Science are common to the natural sciences of Physics, Chemistry and Biology. These practices highlight the ways of thinking and doing inherent in the scientific approach, to equip students with the understanding, skills, and attitudes shared by the scientific disciplines, including an appropriate approach to ethical issues.
The content in this H2 Biology syllabus is organised around four Core Ideas of Biology and two Extension Topics. The Learning Experiences2 refer to a range of learning opportunities selected by teachers to link the biology content of the Core Ideas and Extension Topics with the Practices of Science, to enhance students’ learning of the concepts. Rather than being mandatory, teachers are encouraged to incorporate Learning Experiences that match the interests and abilities of their students and provide opportunities to illustrate and exemplify the Practices of Science, where appropriate. Real-world contexts can help illustrate the biology concepts and their applications. Experimental activities and ICT tools can also be used to build students’ understanding.
The two Extension Topics are based on important emerging biological issues impacting both the local and global contexts. They require students to demonstrate assimilation of the Core Ideas and extend their knowledge and understanding to real-world challenges. Furthermore, Extension Topics will equip students with the necessary knowledge and process skills to make informed decisions about scientific issues. In line with this, the two Extension Topics chosen are (A) Infectious Diseases and (B) the Impact of Climate Change on Animals and Plants. Both Extension Topics take up about 10% of the total H2 Biology curriculum.
Students are expected to study all four Core Ideas and both Extension Topics.
Assessment of Objectives of H2 Biology
The Assessment Objectives of H2 Biology listed below reflect those parts of the Aims and Practices of Science that will be assessed.
A. Knowledge with understanding
Candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge with understanding about:
- scientific phenomena, facts, laws, definitions, concepts and theories
- scientific vocabulary, terminology and conventions (including symbols, quantities and units)
- scientific instruments and apparatus, including techniques of operation and aspects of safety
- scientific quantities and their determination
- scientific and technological applications with their social, economic and environmental implications.
The syllabus content defines the factual materials that candidates need to recall and explain. Questions testing the objectives above will often begin with one of the following words: define, state, name, describe, explain or outline (see the Glossary of Terms).
B. Handling, applying and evaluating information
Candidates should be able (in words or by using symbolic, graphical and numerical forms of presentation) to:
- locate, select, organise, interpret and present information from a variety of sources
- handle information, distinguishing the relevant from the extraneous
- manipulate numerical and other data and translate information from one form to another
- present reasoned explanations for phenomena, patterns, trends and relationships
- make comparisons that may include the identification of similarities and differences
- analyse and evaluate information to identify patterns, report trends, draw inferences, report conclusions
and construct arguments - justify decisions, make predictions and propose hypotheses
- apply knowledge, including principles, to novel situations
- use skills, knowledge and understanding from different areas of Biology to solve problems
- organise and present information, ideas and arguments clearly and coherently, using appropriate language.
These Assessment Objectives above cannot be precisely specified in the syllabus content because questions testing such skills are often based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions testing these objectives may begin with one of the following words: discuss, predict, suggest, calculate or determine.
C. Experimental skills and investigations
Candidates should be able to:
- follow a detailed sequence of instructions or apply standard techniques
- devise and plan investigations which may include constructing and/or testing a hypothesis and select
techniques, apparatus and materials - use techniques, apparatus and materials safely and effectively
- make and record observations, measurements and estimates
- interpret and evaluate observations and experimental data
- evaluate methods and techniques, and suggest possible improvements..
Scheme of Assessment
All candidates are required to enter for Papers 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Paper | Type of Paper | Duration | Weighting % | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Multiple Choice | 1 h | 15 | 30 |
2 | Structured Questions | 2 h | 30 | 100 |
3 | Long Structured and Free-response Questions | 2 h | 35 | 75 |
4 | Practical | 2 h 30 min | 20 | 55 |
Paper 1 (1 h, 30 marks)
This paper will consist of 30 compulsory multiple-choice questions. All questions will be of the direct-choice type with 4 options.
Paper 2 (2 h, 100 marks)
This paper will consist of a variable number of structured questions, all compulsory, including data-based or comprehension-type questions. These include questions which require candidates to integrate knowledge and understanding from different areas of the syllabus.
Paper 3 (2 h, 75 marks)
This paper will consist of a variable number of long structured questions, all compulsory, including data-based or comprehension-type questions and one free-response question of 25 marks. These include questions that assess the higher-order skills of analysing, making conclusions and evaluating information and require candidates to integrate knowledge and understanding from different areas of the syllabus.
Section A (50 marks) will comprise two or more compulsory long structured questions. There will be one or more stimulus materials that may be taken or adapted from a source such as a scientific journal or book. This material may not necessarily relate directly to the content of the syllabus. Questions may require candidates to explain terms used in the passage, analyse data, justify decisions, perform calculations and draw conclusions based on information in the stimulus material.
Section B (25 marks) will comprise two free-response questions, from which candidates will choose one. The quality of scientific argumentation and written communication will be given a percentage of the marks available.
Paper 4 (2 h 30 min, 55 marks)
This paper will assess appropriate aspects of Assessment Objectives C1 to C6 in the following skill areas:
- Planning (P)
- Manipulation, measurement and observation (MMO)
- Presentation of data and observations (PDO)
- Analysis, conclusions and evaluation (ACE).
The assessment of skill area P will have a weighting of 5%, and the skill areas MMO, PDO and ACE will have a weighting of 15%. Candidates will require access to apparatus, as stated in the Confidential Instructions. For some questions, candidates may be allocated a specific time for access to the apparatus. Paper 4 may also include data handling/interpretation questions that do not require apparatus, to test the skill areas of PDO and ACE.
Candidates are NOT allowed to refer to notebooks, textbooks or any other information in the Practical Examination.
Weighting of Assessment Objectives
Assessment Objective | Weighting (%) | Assessment Components | |
|---|---|---|---|
A | Knowledge with understanding | 32 | Papers 1, 2, 3 |
B | Handling, applying and evaluating information | 48 | Papers 1, 2, 3 |
C | Experimental skills and investigations | 20 | Papers 4 |
Full H2 Biology syllabus details can be read in the H2 Biology (Syllabus 9744).

