H2 Chemistry (Syllabus 9729)
H2 Chemistry - Introduction
Candidates will be assumed to have knowledge and understanding of Chemistry at O-Level, as a single subject or as part of a balanced science course.
The H2 Chemistry syllabus is designed to place less emphasis on factual material and greater emphasis on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need for students to develop skills that will be of long-term value in an increasingly technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of factual material which may have only short term relevance.
Experimental work is an important component and should underpin the teaching and learning of Chemistry
Aims
The aims of a course based on this H2 Chemistry syllabus should be to:
- provide students with an experience that develops interest in Chemistry and builds the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary for further studies in related fields
- enable students to become scientifically literate citizens who are well-prepared for the challenges of the 21st century
- develop in students the understanding, skills, ethics and attitudes relevant to the Practices of Science, including the following:
- understanding the nature of scientific knowledge
- demonstrating science inquiry skills
- relating science and society
- develop the way of thinking to explain phenomena, approach and solve problems in chemical systems which involves students in:
- understanding the structure, properties and transformation of matter at the atomic/molecular level and how they are related to each other
- connecting between the submicroscopic, macroscopic and symbolic levels of representations in explaining and making predictions about chemical systems, structures and properties.
Curriculum Framework of H2 Chemistry
The key features of the H2 Chemistry Curriculum comprise Core Ideas and Extension Topics, Practices of Science and Learning Experiences as illustrated in the figure below.
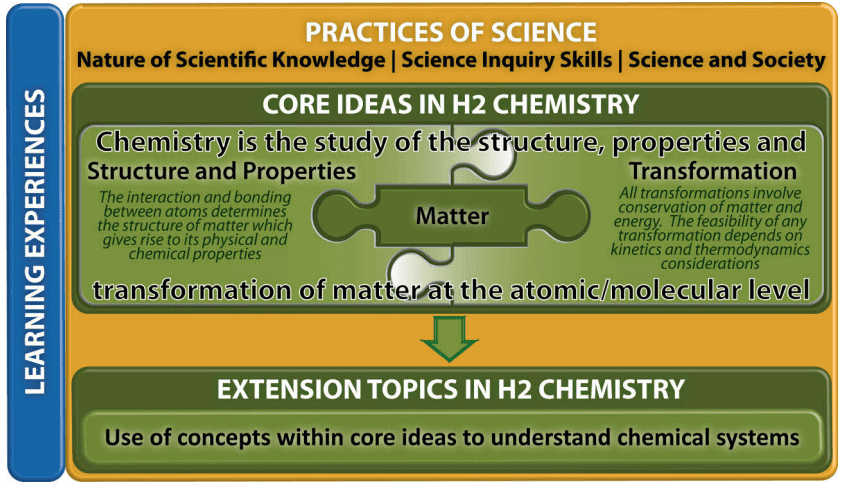
- Core Ideas and Extension Topics
The topics in H2 Chemistry are organised as two levels underpinned by the Practices of Science:- Core ideas: The three Core Ideas of Chemistry are Matter, Structure and Properties, and Transformation.
The concepts in these Core Ideas are interrelated and form the basis on which further learning and understanding of chemical phenomena and reactions is built. - Extension topics: Concepts in the Core Ideas extend into learning different chemical systems such as the chemistry of organic compounds and transition elements. For example, an understanding of concepts of Chemical Bonding and The Periodic Table is extended to the study of the chemistry of transition metals where students learn to appreciate the similarities and differences when comparing with main group metals.
- Core ideas: The three Core Ideas of Chemistry are Matter, Structure and Properties, and Transformation.
- Practices of Science
The Practices of Science are common to the natural sciences of physics, chemistry and biology. These practices highlight the ways of thinking and doing that is inherent in the scientific approach, intending to equip students with the understanding, skills, and attitudes shared by the scientific disciplines, including an appropriate approach to ethical issues. - Learning Experiences
The Learning Experiences refer to a range of learning opportunities selected by teachers to link the chemistry content with the Core Ideas and the Practices of Science to enhance students’ learning of the concepts. Rather than being mandatory, teachers are encouraged to incorporate Learning Experiences that match the interests and abilities of their students and provide opportunities to illustrate and exemplify the Practices of Science,
where appropriate. Real-world contexts can help illustrate the concepts in chemistry and their applications. Experimental activities and ICT tools can also be used to build students’ understanding.
Assessment of Objectives of H2 Chemistry
The Assessment Objectives of H2 Chemistry listed below reflect those parts of the Aims and Practices of Science that will be assessed.
A. Knowledge with understanding
Candidates should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding about:
- scientific phenomena, facts, laws, definitions, concepts and theories
- scientific vocabulary, terminology and conventions (including symbols, quantities and units)
- scientific instruments and apparatus, including techniques of operation and aspects of safety
- scientific quantities and their determination
- scientific and technological applications with their social, economic and environmental implications.
The syllabus content defines the factual knowledge that candidates may be required to recall and explain. Questions testing these objectives will often begin with one of the following words: define, state, name, describe, explain or outline
B. Handling, applying and evaluating information
Candidates should be able (in words or by using symbolic, graphical and numerical forms of presentation) to:
- locate, select, organise and present information from a variety of sources
- handle information, distinguishing the relevant from the extraneous
- manipulate numerical and other data and translate information from one form to another
- analyse and evaluate information to identify patterns, report trends and conclusions, and draw inferences
- present reasoned explanations for phenomena, patterns and relationships
- apply knowledge, including principles, to novel situations
- bring together knowledge, principles, concepts and skills from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context
- evaluate information and hypotheses
- construct arguments to support hypotheses or to justify a course of action
- demonstrate an awareness of the limitations of Chemistry theories and models
These Assessment Objectives cannot be precisely specified in the syllabus content because questions testing such skills may be based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions testing these objectives will often begin with one of the following words: predict, suggest, construct, calculate or determine.
C. Experimental skills and investigations
Candidates should be able to:
- follow a detailed set or sequence of instructions and use techniques, apparatus and materials safely and effectively
- make, record and present observations and measurements with due regard for precision and accuracy
- interpret and evaluate observations and experimental data
- identify a problem, devise and plan investigations, select techniques, apparatus and materials
- evaluate methods and techniques, and suggest possible improvements.
Scheme of Assessment
All candidates are required to enter for Papers 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Paper | Type of Paper | Duration | Weighting % | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Multiple Choice | 1 h | 15 | 30 |
2 | Structured Questions | 2 h | 30 | 75 |
3 | Free Response Questions | 2 h | 35 | 80 |
4 | Practical | 2 h 30 min | 20 | 55 |
Paper 1 (1 h, 30 marks)
This paper consists of 30 compulsory multiple-choice questions. Five to eight items will be of the multiple completion type. All questions will include 4 options.
Paper 2 (2 h, 75 marks)
This paper consists of a variable number of structured questions including data-based questions. All questions are compulsory and answered on the question paper. The data-based question(s) constitute(s) 20–25 marks for this paper.
The data-based question(s) provide(s) a good opportunity to test higher-order thinking skills such as handling, applying, and evaluating information. Some questions will also require candidates to integrate knowledge and understanding from different areas and topics of the chemistry syllabus.
Paper 3 (2 h, 80 marks)
This paper consists of two sections:
- Section A worth 60 marks consisting of 3–4 free response questions, all compulsory. Each question constitutes 15–25 marks.
- Section B is worth 20 marks consisting of two questions, each of 20 marks. Candidates are to answer any one question.
These questions will require candidates to integrate knowledge and understanding from different areas and topics of the chemistry syllabus.
Paper 4 (2 h 30 min, 55 marks)
This paper will assess appropriate aspects of objectives C1 to C5 in the following skill areas:
- Planning (P)
- Manipulation, measurement and observation (MMO)
- Presentation of data and observations (PDO)
- Analysis, conclusions and evaluation (ACE)
The assessment of Planning (P) will have a weighting of 5%. The assessment of skill areas MMO, PDO and ACE will have a weighting of 15%.
The scope of the practical paper is indicated in the Practical Assessment section. The assessment of PDO and ACE may also include questions on data analysis which do not require practical equipment and apparatus.
Candidates will not be permitted to refer to books and laboratory notebooks during the assessment.
Weighting of Assessment Objectives
Assessment Objective | Weighting (%) | Assessment Components | |
|---|---|---|---|
A | Knowledge with understanding | 32 | Papers 1, 2, 3 |
B | Handling, applying and evaluating information | 48 | Papers 1, 2, 3 |
C | Experimental skills and investigations | 20 | Papers 4 |
Full H2 Chemistry syllabus details can be read in the H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)

